Insect Sex: How Do Bugs Know, Work & Determine Their Partners

Introduction
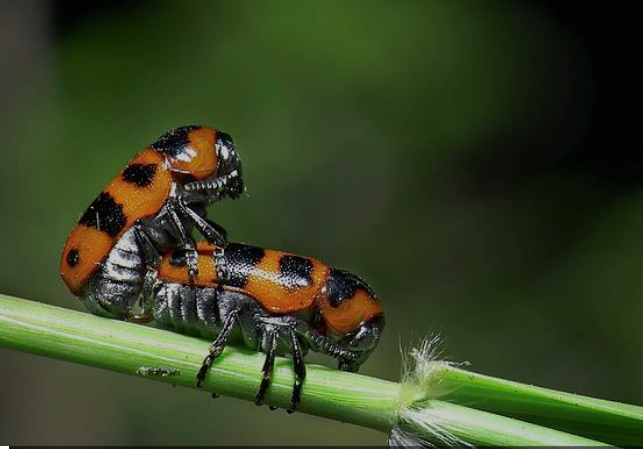
Insects, the tiny creatures that buzz, crawl, and flutter around us, have complex mating rituals and reproductive strategies. While many of us might swat them away without a second thought, the world of insect mating is a fascinating one. This article delves into the intricacies of insect sex, answering questions like how it works, how insects know how to mate, the types of sex determination used, and whether bugs mate for life.
Also Read:- Unveiling the Mysteries of the Camel Spider: Nature, Habitat, and Impact on Humans and Pets in the US
How Does Insect Sex Work?
Insects have a diverse range of reproductive strategies, but most follow a general pattern. Male insects produce sperm, which is transferred to the female during mating. The female then stores the sperm in a specialized organ called the spermatheca. When she’s ready to lay eggs, the stored sperm fertilizes them.
The act of mating can vary greatly among insect species. Some insects, like dragonflies, have elaborate aerial displays, while others, like certain beetles, engage in ground-based combat to win over a mate. The actual act of copulation can last from a few seconds to several hours, depending on the species.
How Do Insects Know How to Mate?
Insects rely on a combination of visual, auditory, and chemical cues to identify and attract potential mates.
- Visual Cues: Many insects use visual signals to attract mates. For instance, fireflies use bioluminescent flashes in specific patterns to signal their availability and species to potential mates.
- Auditory Cues: Crickets and grasshoppers are famous for their songs, which are produced by rubbing their wings together. These songs are species-specific and help females locate suitable males.
- Chemical Cues: Pheromones play a crucial role in insect mating. These are chemical signals released by one individual to affect the behavior of another. Female moths, for example, release pheromones that can attract males from great distances.
What Type of Sex Determination is Used in Insects?
Sex determination in insects is diverse and can be influenced by genetic, environmental, and even social factors. The most common systems are:
- XX-XY System: Similar to humans, where females have two of the same kind of sex chromosome (XX) and males have two distinct chromosomes (XY). This system is found in some insects like grasshoppers.
- XX-X0 System: In this system, females have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have only one (X0). This is seen in certain bugs like bedbugs.
- Haplodiploidy: This is a unique system found in bees, ants, and wasps. Females develop from fertilized eggs and have two sets of chromosomes (diploid), while males develop from unfertilized eggs and have only one set of chromosomes (haploid).
- Environmental Determination: In some insects, environmental factors, such as temperature, can determine sex. For instance, in some butterfly species, the temperature during a critical period of larval development determines whether the individual becomes male or female.
Do Bugs Mate for Life?
While the idea of lifelong partners is romantic, it’s rare in the insect world. Most insects mate with multiple partners throughout their short lives. However, there are exceptions:
- Termites: The king and queen of a termite colony are monogamous and mate for life. They can live for several years, producing millions of offspring during their lifetime.
- Gibbons: While not insects, it’s worth noting that gibbons are among the few animals that practice monogamy, forming lifelong bonds with their partners.
In contrast, many insects, like the praying mantis and redback spider, have extreme mating behaviors where the female consumes the male after mating!
Conclusion
The world of insect mating is as diverse as the insects themselves. From intricate mating dances to complex chemical signals, insects have evolved a myriad of strategies to ensure the continuation of their species. While they might not always mate for life, their reproductive behaviors are a testament to the wonders of evolution and the intricate dance of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Insect Mating
1. How do insects mate?
Insects mate when the male transfers sperm to the female. The female stores this sperm in a specialized organ and uses it to fertilize her eggs when she’s ready to lay them. The mating process can vary greatly among different insect species.
2. How do insects attract mates?
Insects use a combination of visual, auditory, and chemical cues to attract potential mates. This includes visual displays, songs, and the release of pheromones.
3. Do all insects use pheromones for mating?
While many insects use pheromones as a primary method of attracting mates, not all do. The use and type of pheromones can vary widely among different insect species.
4. How do insects determine their sex?
Sex determination in insects can be influenced by genetic, environmental, and social factors. Common systems include the XX-XY system, XX-X0 system, haplodiploidy, and environmental determination.