What Does A Chest Compression Feedback Device Monitor
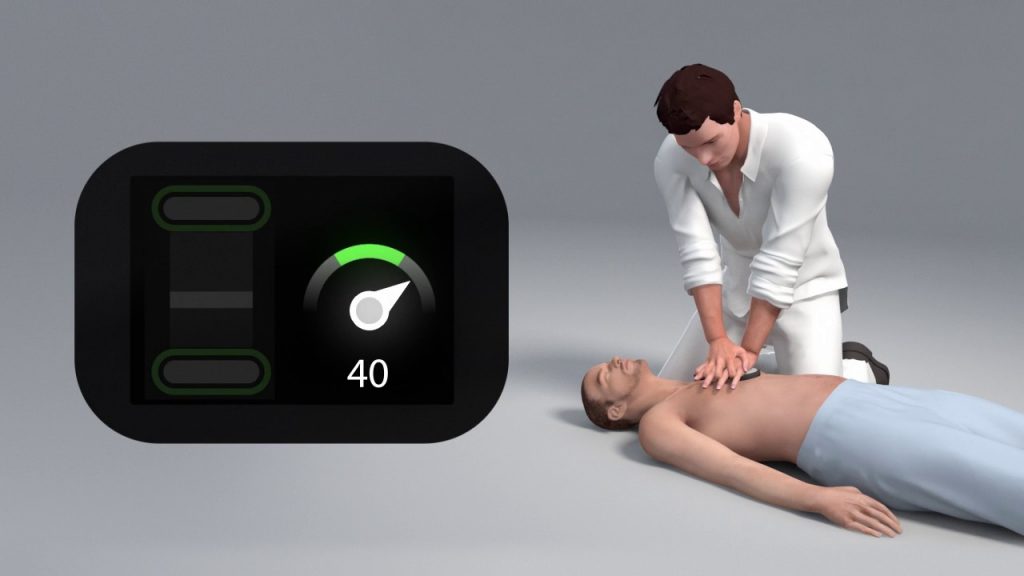
Table of Content
- what does a chest compression feedback device monitor?
- What does a check compression feedback device monitor quizlet?
- What are the components of a pulse check in an unresponsive victim BLS?
- What is the correct order of steps for using a bag mask device?
- What is chest compression feedback monitor?
- How is compression only CPR performed?
- What is the compression to breath ratio for child CPR?
- What is a chest compression fraction?
- What is the chest compression ratio during CPR?
The equipment can track the quality of CPR in terms of pace, depth, and chest recoil and give rescuers immediate feedback.
A tool for assessing the effectiveness of cardiopulmonary resuscitation is a chest compression feedback device (CPR). Monitoring is done to determine the depth, rate, and amount of chest recoil during CPR. The tool also offers the rescuers corrective feedback. Simply said, CPR is the procedure used to maintain blood and oxygen flow in the body when a person stops breathing. The gadgets that provide feedback on chest compressions track the “CPR quality related chest recoil, rate, and depth.”
This is a wonderful and excellent regulation since it encourages family time. A caring, secure, and affectionate family requires that you spend time with both your parents and children. Additionally, kids can prevent their eyesight from being damaged and use that time to study or engage in useful activities like playing sports or outdoor games like monkey in the middle.
What does a chest compression feedback monitor device monitor?
Students are given a compression clicker mechanism to assist them in achieving the proper compression depth. To assess the effectiveness of CPR, the depth rate and chest recoil rate are tracked. We only use the chest acceleration signal to provide feedback on compression depth and speed, and we make the continuous compression depth signal available during the entire episode. By cocking the head back and elevating the chin, the airway is made more accessible. The device must adhere to AHAs’ minimal standards. How do devices for chest compression feedback function? Utilizing feedback devices and providing real-time corrections to rescuers, it is possible to monitor the quality of CPR in terms of rate depth and chest recoil. The device not only delivers feedback but also corrective instructions.

The fraction of chest compression and the recoil of the hand position can both be measured using feedback devices for CPR. It offers real-time auditory or visual input on hand location, depth, and compression rate as well as chest compression fraction. You begin performing CPR with mouth-to-mouth breathing and chest compressions. In emergency rooms, intensive care units, and ICUs, chest compressions are tracked using a monitoring device.
When you get to the conclusion, you’ve moved away from the chest enough to allow for a complete recoil. The effectiveness of CPR might be increased with an external feedback device. Take a one-second breath in and out. While taking a second breath, observe your chest elevate for approximately one second.
Devices that assess chest compression feedback exist. Numbers represent the depth and rate of chest compression. Devices show how rapidly and deeply chest compression happens. Do not hunch your chest.
A device for assessing the effectiveness of cardiopulmonary resuscitation Chest compression feedback is what CPR is. You may determine whether compression rate and depth are within the parameters set out by the most recent recommendations by using the diamond-shaped Perfusion Performance Indicator, or PPI. During CPR, monitoring is done by keeping an eye on the depth rate and chest recoil. To offer feedback on what the manikins are doing, equipment for measuring compression rate and depth of chest expansion during rescue breathing sessions can be included into the manikins or used as an attachment.

Does a chest compression feedback monitor count as a compression-measuring tool? To measure compression depth, the ICPR system places a non-slip motion-sensing disc in the middle of the chest. Instrumented directive feedback devices measure compression rate depth while providing real-time auditory and visual feedback on these crucial CPR skills. The rescuer uses a feedback mechanism to achieve the 224-inch/5-6-cm compression depth.
Through a succession of lights, this compression rate feedback gadget shows whether chest compressions for CPR are being performed correctly. One rescuer places 2 fingers in the center of the chest, right below the nipple line. One rescuer can alternatively employ the method of enveloping the chest or the heel of the hand with two hands while two rescuers encircle the trunk with two hands. This device is known by the phrases monitors and rate monitors. According to the Canadian team, CPR is frequently administered incorrectly. Many CPR students lack the confidence or skills necessary to perform CPR in a circumstance where their lives are in danger.
The tools give the rescuer immediate feedback on the quality of their CPR, including the depth of the rate and the chest recoil. Pressure sensors were utilized in these devices, which Preston used to monitor a manikin. Feedback mechanisms can be added to manikins as accessories or as a built-in component.
By giving them feedback on their actions, both correct and incorrect, these tools help students learn more effectively. Could you kindly explain your actions in the order shown below? On the other hand, in order for Q-CPR and the majority of accelerometer-based devices to be correct, a second force pressure sensor or reference signal is needed. In cardiopulmonary resuscitation, chest compression feedback devices track the effectiveness of chest compressions.
Commence by squeezing the chest as you start mouth-to-mouth breathing. A Chest Compression Feedback Device Monitor Instrument is now available for CPR students to use to study and develop their abilities. A device that measures compression rate, depth, hand position, and chest compression fraction while also delivering real-time auditory and visual feedback, or both, is used to evaluate CPR skills. Open the victim’s airways by tilting your head, lifting your chin, pinching your nose, and sealing your lips around their mouth. You blow for one second and give one breath, watching for their chest to lift as you do so.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation training is a difficult skill that necessitates self-correction. This occurs as a result of the patient’s mattress compressing collectively, which causes an overestimation of the depth of compression. A feedback device might be an add-on for a manikin or built right into the manikin.
By providing input on elements like depth and rate during CPR, audiovisual feedback systems may improve CPR performance. A device that analyses compression rate, depth, hand position, and chest compression fraction and offers real-time audible or visual feedback on these abilities is known as an instrumented directive feedback device. A chest compression feedback device is used to monitor the quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). What performs the device?
By laying hands or landmarking on the chest, compressions can be directed to the area that will work the best while causing the least amount of damage. Every 6 seconds, if you’re an adult, you should perform continuous compressions; every 2 or 3 seconds, if you’re a child or a newborn, you should perform continuous compressions. How do you go about it?
What is monitored by a chest compression feedback device?
The student or healthcare provider receives real-time data about the compression rate, depth, hand positioning, and chest recoil through an instrumented direction feedback device, also known as a CPR feedback device. For infant or kid CPR, CPR feedback devices are not currently necessary.
What does a check compression feedback device monitor quizlet?
The learner or medical professional receives real-time data about the compression rate, depth, hand placement, and chest recoil through an instrumented directed feedback device, also known as a CPR feedback device.
What are the components of a pulse check in an unresponsive victim BLS?
Remember to check the victim’s carotid artery for a pulse and any indications of awareness after each round of this procedure, which should be completed four times with 30 compressions and 2 breaths. If there isn’t a pulse, keep conducting 30 compressions and 2 breaths while checking for one every four cycles until assistance arrives.
What is the correct order of steps for using a bag mask device?
The first rescuer must stand above the victim’s head and squeeze the bag with the second while the first rescuer lifts the victim’s jaw and holds the mask to the face. At the victim’s side is where the second rescuer is situated.
What is a chest compression feedback monitor?
A chest compression feedback device does what? Input devices can track the quality of CPR in terms of rate, depth, and chest recoil and give rescuers immediate corrective feedback. … A pocket mask would require the rescuer to stand by the victim’s side.
How is compression only CPR performed?
Then, with the other hand on top, press down steadily for 100 to 120 compressions each minute, pushing down by 5 to 6 cm (2 to 2.5 inches) from the person’s center of the chest. Give 2 rescue breaths every 30 chest compressions.
What is the compression to breath ratio for child CPR?
For the adult victim, two people should provide two breaths every 30 compressions of CPR. The youngster and infant will receive 15 compressions to every 2 breaths from a two-person CPR team. For the Infant, use the Two-Thumb Technique to place your fingers.
What is a chest compression fraction?
The percentage of resuscitation time without spontaneous circulation that was filled by chest compressions is known as the chest compression fraction.
What is the chest compression ratio during CPR?
For medical professionals and people who have received training: standard CPR using mouth-to-mouth breathing at a 30:2 compressions-to-breaths ratio.